
You may have heard the term "school district" many times over the years. But what is it? They are a special district that operates public primary and secondary schools in a certain area. These districts are either privately managed or overseen by a school board. What makes them special? Learn more about these special purpose districts by reading the following article. You can read the following article to understand how your school system works. You will discover that there are many.
They are all independent
In some US states, independent school district operate independently of any other county, municipality, state, or country. Because they are independent from their parent organizations, they are exempted from the same laws as other school areas. Independent school districts can also be called charter schools. They are often superior to traditional public education districts, regardless their operating style. Let's take a look at their unique characteristics.
They are open to all.
You might be curious about the meaning of "school" and why they exist. Special-purpose districts, also known as school districts, are those created by the states for the purpose of managing public schools. Although there are many differences among public and private schools, one constant is that school districts are part the local government. These districts are funded by local taxes and then managed by elected officials.
They are governed by a board of education
A board of education is an educational governing body for a local school district. It is composed of citizens who are elected by the voters or appointed by them. They act as the eyes and ears for the education system. School boards are responsible for ensuring that public education is high quality and effective in their local communities. The board faces difficult decisions and the scrutiny of the public on a regular basis. But, they also participate in academic achievement. A school board's work can be closely examined by the public. Its members are often close to citizens and voters, and their opinions and suggestions are highly valued.
They are governed according to a mandate from the state
A state mandate (also known as a "mandate") is a state law that specifies which type of education system is responsible for a certain standard. These mandates may be executed by the state's department or county offices for education, as well as school districts. Depending on the state mandate, it may be passed to school districts or delegated at the administrative level to a judge. While mandates may be required by many states, others do not.
They are funded by local taxes
Local taxes help fund school districts. Property taxes are generally the main source of school funding. The millage is the rate at which property owners have to pay taxes. One mill equals 1 dollar of tax. The millage rate for a district is based on the local property tax base. While the state and federal governments match this amount up to a certain point, it is not uniform across all districts.
They can make rules and regulations
A school district is a quasi municipal corporation that the state legislature created to manage public schools. School districts generally have the responsibility of setting rules and regulations for the operation of schools. While school districts are generally organized in a way that minimizes central administration, there are some instances when school districts can have even greater powers. These powers include the power of creating rules and regulations and determining what school activities should be permitted.

They are open to public scrutiny
The District might include information on district needs in a newsletter. Staff and students could be informed of community meetings about a ballot issue. Schools may also have their own community calendar. Some districts may post information about ballot measures on their website, but these may not be as accessible as the district would like. This transparency is crucial for public education. However, the district is not immune to public criticism. It could decide to limit distribution of political materials on public transport.
FAQ
How much does homeschooling cost?
Homeschooling is free. There are no set fees. Some families charge between $0-$20 per lesson. Other families offer no-cost services.
However, homeschooling requires dedication and commitment. Parents should have enough time for their children.
Access to books, materials, and other learning aids is essential. Homeschoolers often need to take advantage of community events and programs to supplement their curriculum.
Parents must think about the cost of transport, tutoring, and other extracurricular activities.
Homeschoolers must also plan ahead to take part in field trips, vacations, or special occasions.
What does it really mean to be an early childhood teacher?
An early childhood teacher must have specific training. Most states require teaching candidates to get certification from state boards in order to be allowed to teach in public schools.
Some states require teachers to pass tests on subjects like math and reading.
Some states require that teachers have completed a minimum number of courses related to early childhood education.
Many states have minimum requirements for teachers. These requirements can differ from one state to another.
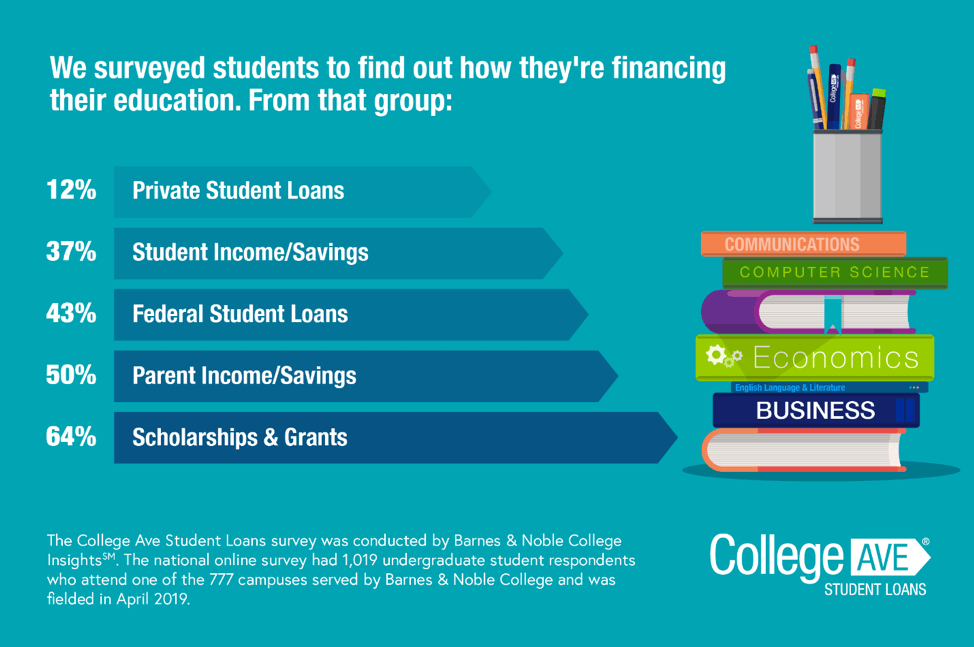
How do you get scholarships?
Scholarships are grants that can be used to pay college costs. There are many types and types of scholarships. These scholarships include:
-
Federal Grants
-
State Grants
-
Student Loans
-
Work Study Programs
-
Financial Aid
Federal grants are directly issued by the U.S. government. Most federal grants require applicants to meet certain requirements. You must, for example, demonstrate financial need.
State grants can be offered by the individual states. Some states offer these funds based on financial need; others award money for specific reasons.
Banks and other lending institutions can issue student loans. Students typically borrow money to cover costs such as tuition and living expenses.
Work-study programs encourage employers to hire qualified student workers. Employers must pay at least the minimum wage to their employees.
Financial aid can help families with low incomes afford college by covering all or part of tuition costs.
How do I select my major?
Students choose their majors based upon their interests. Students may choose to major in the subject they are most passionate about because it is easier than learning something else. Others want to pursue a career for which there are no jobs available. Others choose a major to make money while they study. No matter your reasons for choosing a major, you should consider the type of job that you might be interested in after you graduate.
There are many ways to get information about different fields of study. Talk to your family and friends about their experiences. Look through newspapers and magazines to find out what careers are available. Talk to your guidance counselor at school to learn more about possible careers. Visit Career Services at the local library or community centre. Check out books on various topics from your public library. To search for websites that relate to specific careers, use the Internet.
What do you need to become a teacher in early childhood?
First you need to decide if your career path is in early childhood education. You will need to earn your bachelor's degree if you decide to pursue a career in early childhood education. Some states require that students earn a master’s degree.
You will also likely need to attend classes during the summer months. These courses are about pedagogy, the art of teaching, and curriculum development.
Many colleges offer associate degrees which lead to teaching certificates.
Some schools offer bachelor's or certificates in early childhood education. Others only offer diplomas.
You may not require additional training if you are planning to teach at your own home.
Is it necessary to attend college in order to be an early childhood educator
However, you may want to think about going to college in order to be prepared for a career in the field.
It's important to note that becoming a teacher isn't easy. Each year there are many applicants that are not accepted into programs. In addition, many people quit after just one semester of college.
On top of all this, you still have to meet strict qualifications to become a teacher.
Statistics
- Data from the Department of Education reveal that, among 2008 college graduates, 92.8 percent of humanities majors have voted at least once since finishing school. (bostonreview.net)
- In most developed countries, a high proportion of the population (up to 50%) now enters higher education at some time in their lives. (en.wikipedia.org)
- They are more likely to graduate high school (25%) and finish college (116%). (habitatbroward.org)
- Among STEM majors, that number is 83.5 percent. (bostonreview.net)
- And, within ten years of graduation, 44.1 percent of 1993 humanities graduates had written to public officials, compared to 30.1 percent of STEM majors. (bostonreview.net)
External Links
How To
What is vocational education?
Vocational education is an educational program that prepares students to work after high school and college. It teaches them specific skills for specific jobs (such as welding). You can also get on-the job training through apprenticeship programs. Vocational education differs from general education because it focuses on preparing individuals for specific careers rather than learning broad knowledge for future use. The goal of vocational education is not necessary to prepare people for university study but to help them find jobs upon graduation.
Vocational education is available at all levels of education, including primary, secondary, high school, college, universities, technical institutes as well as trade schools, community colleges and junior colleges. There are also many specialty schools like nursing schools and law schools, legal schools, medical schools and dental schools as well as veterinary medicine, veterinary medicine, firefighting, police academies and military academies. Many of these provide both academic instruction and practical experience.
Over recent decades, there have been significant investments made in vocational education by many countries, including Australia, Denmark (Finland), Germany, Ireland and Japan. The effectiveness of vocational training is still a controversial topic. Some critics argue that it does little to improve students' employability; others argue that it provides useful preparation for life after school.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (47% of American adults are currently holding a postsecondary certificate/degree related to their current job), this figure is higher among those with more education. This figure is higher among those with more education: 71% of workers aged 25-29 with a bachelor's degree or higher are currently employed in fields requiring postsecondary credentials.
According to the BLS, nearly half of America's adult population held at least one postsecondary credential in 2012. About one-third of Americans held a two-year associate degree, while about 10 percent held a four-year bachelor's degree. One in five Americans has a master's or doctorate.
For those with a bachelor’s degree, the median annual income was $50,000. This is compared to $23,800 if you don't have one. For advanced degrees, the median annual wage was $81,300.
For those who did not complete high school, the median wage was only $15,200. For those who did not complete high school, the median annual salary was only $15,200.